Objective See Little Snitch
To put in perspective, the last upgrade of Little Snitch (version 2 to 3) was Fall of 2013, to support Mavericks 10.9. That was nearly four years ago guys. The current macOS is 10.12, so Little Snitch v3 has supported FOUR MAJOR RELEASES OF MACOS and a fifth one on the way in that time with LS v3. Apr 01, 2020 Little Snitch 4.5 Crack helps you to see, that is invisible for you. It displays the internet connection, which you cannot see. It provides you authentic control over this internet connection. You can see your Mac’s network connection from three views, a list of application servers, web of connection throughout the world and one-hour history.
Turn it up and you have a grimy knave of twisting.The FATNESS knob boosts the initial signal by as much as 30dB while at the same time adding complex saturation, which is subtle distortion caused by introducing upper harmonics to the fundamental tone. Vocal doubler vst free download. Utilize the Sausage Fattener on a solitary channel with direct settings as a melodic compressor. With those apparently basic parameters, you can make heaps of various sounds.
In order to perform its duty, Little Snitch needs to add components to a very low level of the operating system, which also need to be registered and unregistered with the system. It is therefore not sufficient to just remove all of Little Snitch’s application bundles. Instead, Little Snitch Uninstaller must be run.
Little Snitch is a host-based application firewall for macOS.It can be used to monitor applications, preventing or permitting them to connect to attached networks through advanced rules. It is produced and maintained by the Austrian firm Objective Development Software GmbH. 'Little Snitch informs you whenever a program attempts to establish an outgoing Internet connection. You can allow or deny these connections, or define rules to handle future attempts automatically. Little Snitch reliably prevents your private data from being sent out to the Internet without your knowledge.' Oct 08, 2019. In the list you should see 'Little Snitch Helper'. It too should be checked ON. Also, when installing or updating Little Snitch, several extensions are installed into the system. Be sure something else installed in your system isn't blocking them. The usual routine in these matters is to UNinstall the app entirely, then REinstall. Feb 24, 2019 It seems very simple compared to Little Snitch, however, seems to do a very similar job -without some of the 'advanced' features. 2 things I miss already: - is the network monitor in the menu bar. With Little Snitch, you'd have a green bar for downstream and red bar for upstream, each with the data transfer speed as well. Jun 29, 2018 Little Snitch is a popular Mac app that detects outbound connections and lets you set up rules to block those connections. Once installed, Little Snitch monitors your internet traffic and every time it detects an outbound connection, for example, Adobe Reader trying to access the internet.
Little Snitch Uninstaller
The easiest way to open the Little Snitch Uninstaller is to drag Little Snitch Configuration from the Applications folder to the trash. Little Snitch’s background processes notice this and automatically start the uninstaller that is located in /Library/Little Snitch/Little Snitch Uninstaller.app.
So you can start DEV-C Download FileHippo link below.Overview Of DEV-C Windows:They also learn new languages to keep themselves up-to-date. An IDE is a featured environment that supports, runs and produces the desired result for writing a language. Dev c latest version 5.11 free download full. The first thing you need to write a program in any language is a platform to write and execute the code.
Alternatively, the Little Snitch Uninstaller can be found in the Little Snitch .dmg disk image file, next to the Installer. If you don’t have the disk image at hand, you can always download the current version from our website.
The uninstallation process itself is straight forward, with only one option to choose: Whether you want to remove your rules and settings or not. After the process is finished, you must restart your computer.
If you enable the option to remove rules and settings, the Uninstaller deletes all your system-wide configuration and rules files (also any files from older Little Snitch installations), including the file that stores your license information, as well as the configuration files, rules files and log files for the user executing the Uninstaller.
List of paths
Little Snitch creates files under the following paths:
The “~” (tilde) sign refers to your user’s home folder.
Please note that the Uninstaller does more than move the application bundles to the trash and delete the configuration files. If you really want to remove Little Snitch completely from your system it is highly recommended to use the provided uninstallation application.
Was this help page useful? Send feedback.
© 2016-2020 by Objective Development Software GmbH
When processes exchange data with remote servers, you may want to know what data they actually send and receive. You can use a network sniffer like Wireshark, but these tools record traffic of your entire computer, not just a particular process. Filtering out the relevant data is tedious.
Network Monitor offers an option to record all traffic for a particular process in PCAP format.
Start and stop a capture
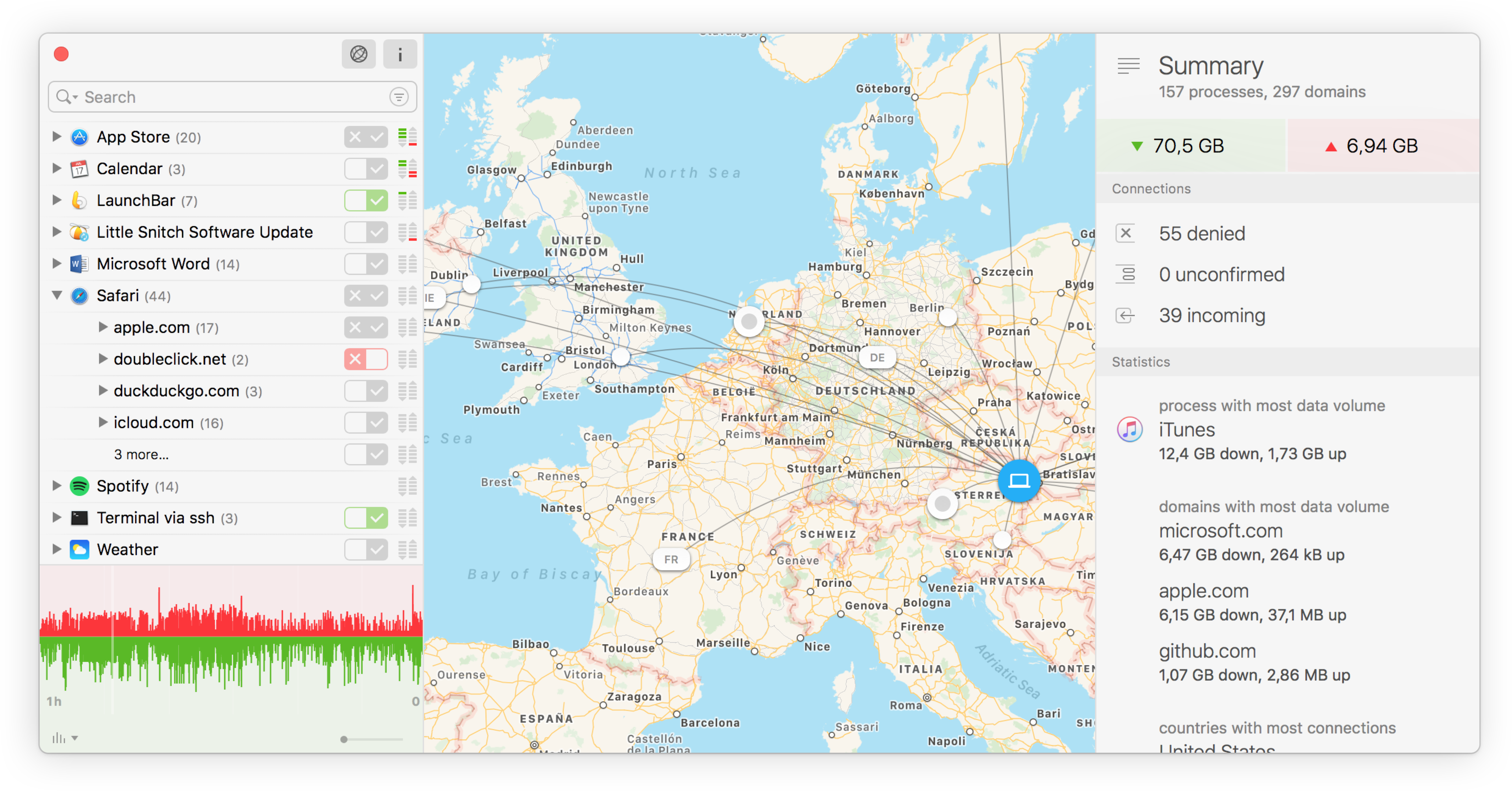
To start capturing traffic of a certain process, right-click the process in Network Monitor’s Connection List and choose Capture Traffic of … from the context menu. Little Snitch starts capturing immediately while you choose a name for the file. Little Snitch can run any number of simultaneous traffic captures.
To stop a running capture, you can either click Little Snitch’s status menu item (where a red recording indicator is blinking) and choose Stop Capture of … or right-click the connection being captured in the Connection List and choose Stop Capture from the context menu.
Interpret captured data
In order to understand the results of a traffic capture, you must know that Little Snitch intercepts traffic at the application layer, not at the network interface layer as other sniffers do. This is what distinguishes Little Snitch from conventional firewalls, after all. At this layer, however, it is not yet known via which network interface the data will be routed (which sender Internet address will be used) and sometimes it is not known which sender port number will be used. It is also not known whether and how the data will be fragmented into packets. All this information is required in order to write a valid PCAP file. Little Snitch simply makes up the missing information. It fakes TCP, UDP, ICMP, IP and even Ethernet protocol headers. Missing information is substituted as follows:
- Ethernet (MAC) address – Sender and recipient address are both set to 0.
- Local IP (v4 or v6) address – Numeric Process-ID of process.
- Local TCP/UDP port number – Kernel’s socket identification number.
- Packets are always generated as large as the protocol allows (not as large as the network would allow).
Since all network protocol headers are made up, it is not possible to debug network problems (such as lost packets or retries) with these traffic captures. If you need to debug at the protocol header level, use the tcpdump Unix command or Wireshark instead.
Objective See Little Snitch Movie
Was this help page useful? Send feedback.
© 2016-2020 by Objective Development Software GmbH